8 Types of Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS): A Deep Dive
by Gary Higginbothe, Kardex-Remstar
Several material handling equipment manufacturers design, engineer and manufacture a wide variety of self-contained, goods-to-person, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS). With the focus shifting from picking pallets and cases to picking individual items or “eaches”, there has been an explosion of types of ASRS technologies available in the market to help warehouse, distribution and manufacturing operations make this change.
The ASRS technologies on the market handle different volumes, types, and velocities of non-palletized inventory at variable speeds to accommodate fluctuating throughput demands. When considering the options, keep in mind both the storage density your facility needs as well as your throughput goals.
Categories of Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS)
These 8 ASRS technologies can be broken down into three major categories based on how they deliver goods:
- Shelf based picking – an entire shelf or tray of product is delivered to an operator
- Bin based picking – an individual bin or tote of product is delivered to the operator
- Robotic picking – robots are used to deliver products to an operator
Shelf and Tray Picking ASRS Technologies
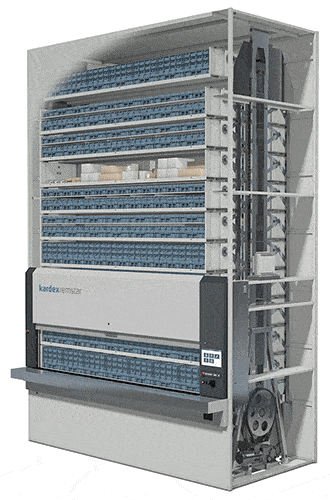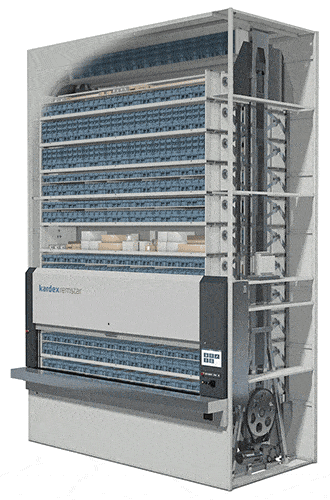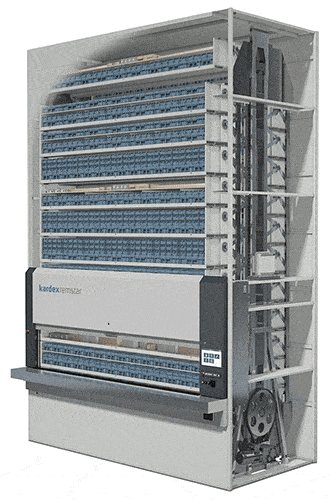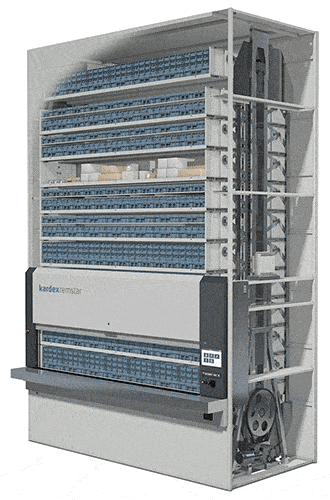
#1 Vertical Lift Modules (VLMs)
The most flexible technology in this category, the Vertical Lift Module is engineered to automatically adjust when your inventory changes. With trays capable of handling up to 2,200 pounds, these enclosed dynamic storage solutions consist of two columns of trays with an inserter/extractor in the center.
The inserter/extractor automatically locates and retrieves stored trays of slow- to medium- velocity items from both columns and presents them to the operator at a waist-high pick window with throughput rates from 125 to 350 items per hour in standard systems. VLMs can be integrated with sophisticated batching stations for even faster picking or integrated with robotic picking technologies for fully automated operations.
Download the Vertical Lift Module Quick Facts PDF
Systems used to store the heaviest items can be equipped with automatic tray extractors and an overhead crane and hoist to help operators handle and maneuver their picks. Because the height of the items placed in each storage tray is measured as it is put away, the VLM stores the trays dynamically—as close as one inch apart—to maximize storage density, saving up to 85% floor space. The VLM is a great technology choice for businesses with changing inventory sizes.
#2 Vertical Carousel Modules
The Vertical Carousel Module has been around for decades. Comprised of a series of carriers attached to a chain drive, a motor powers the carriers’ bi-directional travel in a vertical loop around a track—similar to a Ferris wheel. These automated storage and retrieval systems deliver slow-to medium-velocity items safely and quickly to an ergonomically positioned work counter at the operator’s command. Manufacturers add new bells and whistles with each revision, but the heart of the technology remains the same.
Download the Vertical Carousel Module Quick Facts PDF
Offering throughput at rates of 100 to 400 lines per hour, higher rates can easily be achieved with the addition of light-directed picking technologies and batching stations that allow picking of multiple orders simultaneously. Offering capacities of 1,430 pounds per carrier, the Vertical Carousel Module is a reliable and cost-effective solution that shouldn’t be overlooked.
#3 Horizontal Carousel Modules
Horizontal Carousel Modules consist of highly dense storage bins mounted on an oval track which rotates horizontally to deliver slow- to medium-moving product storage locations to an operator, these automated storage and retrieval systems handle both items and cases with a maximum weight capacity of 2,000 pounds per carrier.
To generate maximum picking speed and throughput, they are often installed in groups, known as pods. This allows a picker to access product from one carousel while others spin to queue up the next required item, yielding throughput rates up to 600 lines picked per hour—achievable with light-directed picking technologies and batching stations that allow simultaneous fulfillment of multiple orders. In addition, Horizontal Carousel Modules offer excellent space utilization and high storage density. These units can also be equipped with an automated door system, creating an enclosed solution.
Bin and Tote Delivery ASRS Technologies
#4 Crane-Based AS/RS
This AS/RS system involves a crane-mounted load handling device dedicated to each extremely dense rack aisle.The cranes travel either on rails or wheels with fast acceleration speeds to deliver product to the operator via a workstation located at the end of the aisle. Traditionally, there were two main types of Crane-based ASRS: mini-load (for eaches and cases) and unit-load (for full or mixed entire pallet storage). In response to companies looking for more flexibility, a new genre of ASRS emerged – a mid-load. A mid-load address both mini-load and unit-load requirements in a single solution. The pioneer in this area is Integrated Systems Design (ISD).
#5 Vertical Buffer Modules (VBMs)
The vertical buffer module is a bin handling system designed for smaller applications (under 10,000 totes or 25,000 SKUs) that often can’t cost justify a large, expensive system. The VBM consists of an enclosed shelving system with a movable mast running down a center aisle for picking and storage of totes. The unit is designed to be able to work ahead of the operator and queue up the next pick for maximum throughput of the system.
Totes can be delivered to an ergonomic turntable picking station or can be automatically handled via inbound and outbound conveyor. The machine can also be configured with a manual station for replenishment of totes during picking operations. Picking never needs to be interrupted for replenishment activities.
Multiple units can be connected via conveyor and totes can be delivered to remote picking stations. The system is designed to be modular, scalable and highly energy efficient.
Robotic Delivery ASRS Technologies
#6 Shuttle Systems/Pallet Runner
This dynamic storage solution uses robotic shuttles to travel independently from level to level, riding on narrow rails at each storage level. These systems store more pallets and move them faster through a warehouse than traditional storage methods. RadioShuttle is one example of a semi-autonomous system used to maximize storage space.
Most robotic shuttle systems are modular, scalable and flexible—meaning they can be expanded with minimal structural modifications as business needs change. For more information on pallet shuttles, contact your local expert.
#7 Robotic Cube Storage
Using the newest type of ASRS technology, robotic cube storage, all inventory is placed into bins that are neatly stacked on top of each other inside a cube. Smart robots work at the top of the cube to shuffle, sort and retrieve bins and deliver them to a workstation (port) as needed.
All robots work independently on the same grid (cube), wirelessly connected to the system and charge themselves when not in use. The controller and software act as the command center providing traffic algorithms and keeping track of everything. Robotic cube storage systems are modular – it’s easy to add robots or workstations as throughput demands fluctuate. The system is also configurable as the grid can be built to any shape or size warehouse.
#8 Floor Robots (AGVs/AMRs)
Why go to the shelving when the shelving can come to you? This solution stores inventory on portable storage shelving that is retrieved and transported from storage to an operator access area by a fleet of autonomous, mobile robots. After the operator selects the required item or items from the shelf, the robot returns it to storage.
Ideal for slow to medium velocity inventory, throughput ranges from 100 to 300 lines per hour and is dependent on the number of robots in the system. Throughput can also be expanded easily with the addition of more robots. The standard weight capacity of 1,000 pounds per shelving system can be increased with the heavy-duty model handling up to 3,000 pounds per shelving unit.
There are two types of floor robots – AGVs and AMRs – and while they technologies are similar, there are some key differences. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are good for repetitive and consistent tasks. They are guided by wires, magnetic strips or sensors that are put onto the facility floor. They then travel only along the marked, predetermined routes. While they can detect obstacles in the route, they are unable to travel off the predetermined path to navigate around them.
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) have onboard software intelligence allowing these floor robots to navigate through a facility using maps (similar to how the GPS in your car works). Using the onboard maps combined with sensors and cameras, an AMR can survey the area and plan the best route to get from point A to point B in the warehouse while navigating around obstacles in its path.
Which Type of Automated Storage is the best fit for your operations?
The ideal solution will often include multiple goods-to-person automation technologies, strategically matching the system to the different inventory profiles and handling characteristics required to create a complete, hybrid solution. It’s important to work with the right team to help determine what technologies will be best for your business. Feel free to contact Andersen Material Handling for more information or to schedule a full systems evaluation.